In industrial piping systems, flanges serve as critical connection points that enable assembly, disassembly, maintenance, and inspection of pipeline networks. Understanding the different types of flanges used in piping is essential for engineers, project managers, and maintenance professionals working across industries. This comprehensive guide explores pipe flange types, their applications, specifications, and selection criteria to help you make informed decisions for your projects.
What Are Stainless Steel Pipe Flanges?
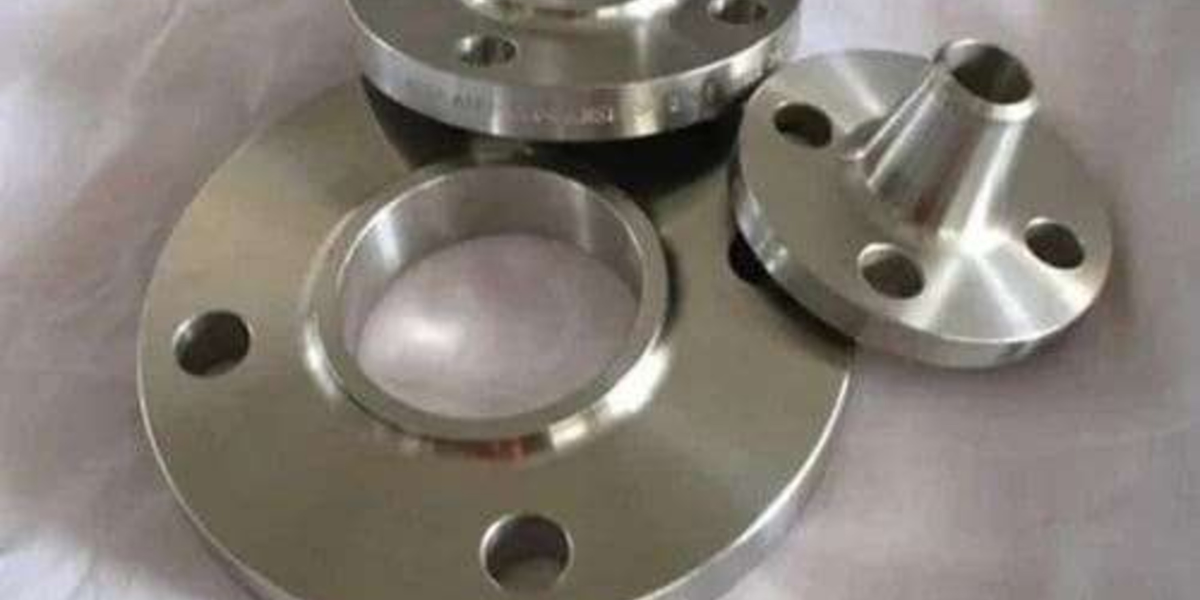
A stainless steel pipe flange is a flat, circular component with bolt holes that connects pipes, valves, pumps, and other equipment in a piping system. These flanges create a bolted joint that can be easily disassembled for inspection, cleaning, or modification without cutting the pipe. Stainless steel flanges offer superior corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, and durability, making them the preferred choice for demanding industrial applications.
Stainless steel pipe flanges can be utilized as plates meant to cover or close the end of a pipe (known as blind flanges). They are considered integral components of internal systems that support mechanical parts and various process equipment, providing access points and connection interfaces throughout complex piping networks.
Understanding Different Types of Flanges Used in Piping
The different types of flanges used in piping systems are designed to accommodate various operating conditions, installation requirements, and maintenance needs. Each pipe flange type offers specific advantages in terms of strength, ease of installation, cost-effectiveness, and performance characteristics. Let’s explore the most common pipe flange types in detail.
1. Weld Neck Flanges: The High-Pressure Solution
Weld neck flanges represent one of the most robust pipe flange types available. These stainless steel flanges feature a long tapered hub that gradually transitions from the flange thickness to the pipe wall thickness, providing excellent stress distribution and resistance to dishing or distortion.
Key Features of Weld Neck Flanges
The tapered hub design of weld neck stainless steel pipe flanges offers several critical advantages. The gradual transition minimizes stress concentration at the flange-to-pipe junction, making them ideal for high-pressure, high-temperature applications. The full-penetration butt weld connection provides maximum strength and leak-proof integrity.
Applications
Weld neck flanges are extensively used in critical service lines including:
- High-pressure steam systems
- Oil and gas transmission pipelines
- Petrochemical process equipment
- Power generation facilities
- Offshore platforms and subsea installations
The structural integrity of weld neck stainless steel flanges justifies their higher cost in applications where safety and reliability are paramount.
2. Slip-On Flanges: Economic and Versatile
Slip-on flanges are among the most economical pipe flange types, characterized by their simple design and ease of installation. These stainless steel pipe flanges slide over the pipe end and are welded both inside and outside to create a secure connection.
Installation Advantages
Stainless steel slip-on flanges offer significant installation benefits. The ability to slide the flange over the pipe allows for easier alignment before welding, reducing installation time and labor costs. These flanges require two fillet welds (inside and outside) rather than the groove weld required for weld neck flanges.
Customization Options
While slip-on stainless steel flanges typically come in round form, they can also be manufactured and customized in square and rectangular forms to accommodate special equipment configurations or space constraints in complex piping systems.
Applications
Slip-on flanges are commonly used in:
- Low to medium pressure applications
- Non-critical service lines
- Water distribution systems
- HVAC piping
- General industrial piping where cost efficiency is prioritized
3. Socket Weld Flanges: Small-Bore Specialists
Socket weld flanges are specialized pipe flange types designed primarily for small-bore, high-pressure piping systems. These stainless steel flanges feature a recessed area (socket) into which the pipe is inserted before being fillet welded.
Design Benefits
Stainless steel socket weld flanges are easily accessed for inspection, cleaning, or modification, making them ideal for systems requiring regular maintenance. The socket design provides proper alignment and eliminates the need for beveling pipe ends, simplifying installation in small-diameter applications.
Smooth Flow Characteristics
The internal construction of socket weld stainless steel pipe flanges creates a smooth bore that minimizes turbulence and pressure drop, making them excellent for instrumentation and process control applications.
Applications
Socket weld flanges excel in:
- Instrumentation piping and gauge lines
- Small-bore process piping (typically 2 inches and smaller)
- High-pressure sampling systems
- Chemical injection points
- Analyzer connections
4. Threaded Flanges: No-Weld Solutions
Threaded flanges represent pipe flange types that utilize internal threads to connect to externally threaded pipes. These stainless steel flanges enable assembly without welding, making them valuable in situations where hot work is restricted or impractical.
Installation Flexibility
Threaded stainless steel pipe flanges can be attached to piping systems by threading rather than welding, providing flexibility in areas where welding is prohibited due to fire hazards, explosive atmospheres, or facility regulations. They’re particularly useful in maintenance access points and temporary installations.
Limitations and Applications
While convenient, threaded connections are generally limited to smaller sizes and lower pressures compared to welded pipe flange types. They’re commonly used in:
- Low-pressure utility piping
- Temporary installations
- Explosive or flammable environments
- Instrumentation connections
- Maintenance access points in existing systems
5. Lap Joint Flanges: Maintenance-Friendly Design
Lap joint flanges, used in conjunction with stub ends, represent unique pipe flange types that facilitate easy alignment and frequent disassembly. These stainless steel flanges consist of two components: a stub end that welds to the pipe and a loose backing flange that can rotate freely.
Component Design
Stainless steel stub end flanges are attached to the piping system by welding, while the backing flange remains loose, allowing rotation for bolt hole alignment. This design significantly simplifies installation when connecting to existing equipment or when dealing with misalignment issues.
Cost Optimization
The lap joint design allows the use of expensive alloy materials (like stainless steel) for the stub end that contacts the process fluid, while the backing flange can be made from less expensive carbon steel, reducing overall system costs without compromising corrosion resistance.
Applications
Lap joint stainless steel pipe flanges are ideal for:
- Systems requiring frequent dismantling
- Lined piping systems
- Situations with bolt hole alignment challenges
- Cost-sensitive projects with corrosive fluids
- Rotating equipment connections
6. Blind Flanges: Termination and Access Points
Blind flanges are solid pipe flange types without a bore opening, used to close pipe ends or vessel nozzles. These stainless steel flanges provide permanent or temporary closures while maintaining system pressure integrity.
Functional Versatility
A stainless steel pipe flange used as a blind flange serves multiple purposes: permanent pipe termination, temporary closure during testing or commissioning, future expansion provisions, and maintenance access points. They must withstand full system pressure while providing a leak-tight seal.
Testing and Maintenance Applications
Blind stainless steel flanges are essential for:
- Hydrostatic testing of piping systems
- Future expansion tie-in points
- Equipment access openings
- Pipeline terminations
- Vessel inspection ports
7. Orifice Flanges: Specialized Measurement Solutions
Orifice flanges are specialized pipe flange types designed to hold orifice plates for flow measurement. These stainless steel pipe flanges feature special pressure tapping connections and internal sealing grooves.
Measurement Capability
Orifice stainless steel flanges incorporate pressure taps on either side of the orifice plate location, allowing differential pressure measurement for accurate flow rate determination. They’re precision-manufactured to ensure consistent orifice plate positioning.
Applications
These specialized pipe flange types are used in:
- Flow measurement systems
- Custody transfer applications
- Process control and monitoring
- Pipeline metering stations
- Regulatory compliance measurements
8. Reducing Flanges: Size Transition Solutions
Reducing flanges combine the functions of a flange and a reducer in a single component. These stainless steel flanges enable direct connection between different pipe sizes without requiring separate reducer fittings.
Space and Cost Savings
Reducing stainless steel pipe flanges eliminate the need for separate reducing components, saving installation space, reducing material costs, and minimizing potential leak points in the system.
Applications
Reducing pipe flange types are commonly used in:
- Pump and equipment connections
- Size transitions in manifold systems
- Branch connections from headers
- Equipment nozzle connections
- Space-constrained installations
9. Long Weld Neck Flanges: Extended Hub Design
Long weld neck flanges are specialized pipe flange types featuring extended hub lengths for specific applications. These stainless steel flanges accommodate insulation requirements or provide additional reinforcement.
Design Advantages
The extended hub of long weld neck stainless steel pipe flanges allows clearance for insulation or pipe coating, prevents cold spots in cryogenic service, and provides additional stiffness in critical applications.
Applications
Long weld neck pipe flange types serve:
- Insulated piping systems
- Cryogenic applications
- High-vibration environments
- Critical pressure vessel connections
- Special reinforcement requirements
10. Expander Flanges: Outlet Size Increase
Expander flanges are pipe flange types that increase the outlet size compared to the inlet. These stainless steel flanges combine the functions of a flange and an expander fitting.
Applications
Expander stainless steel pipe flanges are used in:
- Equipment outlet connections
- Pressure drop management
- Velocity reduction applications
- Pump discharge configurations
Pressure Ratings for Different Types of Flanges Used in Piping
Gaskets for stainless steel flanges are designed to cater to specific pressure ratings, which determine the maximum operating pressure the flange can safely handle. Understanding these ratings is crucial when selecting appropriate pipe flange types for your application.
ANSI/ASME Pressure Classes
Stainless steel pipe flanges manufactured to ANSI standards are available in the following pressure classes:
- Class 150 LBS: For pressures up to 285 psi at ambient temperature
- Class 300 LBS: For pressures up to 740 psi at ambient temperature
- Class 400 LBS: For pressures up to 990 psi at ambient temperature
- Class 600 LBS: For pressures up to 1480 psi at ambient temperature
- Class 900 LBS: For pressures up to 2220 psi at ambient temperature
- Class 1500 LBS: For pressures up to 3705 psi at ambient temperature
- Class 2500 LBS: For pressures up to 6170 psi at ambient temperature
These pressure ratings decrease as temperature increases, so always consult pressure-temperature rating charts for your specific service conditions.
DIN/EN Pressure Ratings
European standard stainless steel flanges follow PN (Pressure Nominal) ratings:
- PN6: 6 bar (87 psi)
- PN10: 10 bar (145 psi)
- PN16: 16 bar (232 psi)
- PN25: 25 bar (363 psi)
- PN40: 40 bar (580 psi)
- PN64: 64 bar (928 psi)
JIS Pressure Ratings
Japanese Industrial Standard stainless steel pipe flanges use K-class ratings:
- 5K: 5 kg/cm² (71 psi)
- 10K: 10 kg/cm² (142 psi)
- 16K: 16 kg/cm² (228 psi)
- 20K: 20 kg/cm² (284 psi)
- 30K: 30 kg/cm² (427 psi)
- 40K: 40 kg/cm² (569 psi)
- 63K: 63 kg/cm² (896 psi)
Key Features of Stainless Steel Flanges
Regardless of the specific pipe flange types selected, stainless steel flanges offer consistent performance advantages:
High Strength
Stainless steel pipe flanges provide exceptional tensile and yield strength, enabling them to withstand high bolt loads and system pressures without deformation or failure.
Resistance Against Corrosion
The chromium oxide passive layer on stainless steel flanges delivers outstanding corrosion resistance against atmospheric exposure, chemical attack, and aggressive process media.
Resistance Against High Pressure
Properly selected pipe flange types in stainless steel materials can safely handle pressures up to 6,170 psi (Class 2500), making them suitable for the most demanding applications.
Resistance Against High Temperature
Stainless steel pipe flanges maintain mechanical properties and dimensional stability at elevated temperatures, with certain grades performing reliably up to 1500°F or higher.
Dimensional Stability
Stainless steel flanges resist creep, thermal distortion, and stress relaxation, maintaining critical dimensions throughout their service life.
Longer Service Life
The combination of corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, and dimensional stability results in extended service life, often exceeding 30-50 years in appropriate applications.
Resistance Against High Mechanical Stress
Stainless steel pipe flanges withstand cyclic loading, vibration, thermal expansion stresses, and external forces without fatigue failure.
Specifications of Stainless Steel Flanges
Size Range
ASME B16.5 stainless steel flanges are available in sizes ranging from 1/2″ (15 NB) to 48″ (1200 NB), with larger sizes available under ASME B16.47. Metric equivalents range from DN10 to DN5000.
Manufacturing Standards
Different types of flanges used in piping are manufactured according to various international standards:
ANSI/ASME Standards:
- ASME B16.5: Pipe flanges and flanged fittings NPS 1/2 through NPS 24
- ASME B16.47 Series A: Large diameter flanges (MSS SP-44)
- ASME B16.47 Series B: Large diameter flanges (API 605)
- ASME B16.48: Line blanks
European Standards:
- BS 4504: British Standard flanges
- BS 10: Flanges and bolting for pipes, valves and fittings
- EN 1092: Flanges and their joints
- DIN: German Institute for Standardization specifications
Other International Standards:
- GOST: Russian standard flanges
- UNI: Italian standard flanges
- JIS: Japanese Industrial Standards
Material Grades
Stainless steel pipe flanges are available in numerous grades:
Austenitic Stainless Steels:
- 304/304L: General purpose, excellent corrosion resistance
- 316/316L: Enhanced corrosion resistance with molybdenum
- 321: Titanium-stabilized for high-temperature service
- 347: Columbium-stabilized for elevated temperatures
- 310S: Superior high-temperature oxidation resistance
- 904L: Super-austenitic for highly corrosive environments
Duplex Stainless Steels:
- 2205: High strength with excellent corrosion resistance
- 2507: Super duplex for extreme environments
Precipitation Hardening Grades:
- 17-4 PH: High strength with good corrosion resistance
Facing Types
Pipe flange types are available with various facing configurations:
Raised Face (RF): Most common, features a raised surface (1/16″ or 1/4″) that compresses the gasket.
Flat Face (FF): Completely flat surface, used primarily with cast iron flanges or low-pressure applications.
Ring Type Joint (RTJ): Machined groove for metal ring gaskets, used in high-pressure, high-temperature service.
Tongue and Groove (T&G): Interlocking faces that provide self-alignment and prevent gasket blowout.
Male and Female (M&F): Similar to tongue and groove with different dimensions.
Selecting the Right Pipe Flange Types
Choosing appropriate pipe flange types requires careful consideration of multiple factors:
Operating Conditions
- Pressure: Select pressure class adequate for design pressure
- Temperature: Verify material grade and pressure rating at operating temperature
- Fluid Characteristics: Consider corrosivity, toxicity, and flammability
- Cyclic Service: Account for thermal cycling and pressure fluctuations
Installation Requirements
- Welding Capability: Determine if welding is permitted or practical
- Space Constraints: Consider physical dimensions and clearances
- Alignment Needs: Evaluate ease of bolt hole alignment
- Future Maintenance: Plan for disassembly and inspection requirements
Economic Considerations
- Initial Cost: Balance material and installation costs
- Lifecycle Costs: Consider maintenance, replacement, and downtime costs
- Material Optimization: Use lap joint designs to reduce expensive alloy usage
- Standardization: Minimize variety to reduce inventory costs
Code Compliance
- Project Specifications: Meet client and project requirements
- Regulatory Standards: Comply with local codes and regulations
- Industry Standards: Follow industry-specific requirements (ASME BPE, 3-A, etc.)
- Client Preferences: Accommodate end-user standards and practices
Installation Best Practices for Different Types of Flanges Used in Piping
Proper installation ensures optimal performance across all pipe flange types:
Surface Preparation
- Clean flange faces to remove rust, scale, and debris
- Inspect flange faces for damage, scratches, or warping
- Verify gasket seating surfaces are smooth and flat
- Remove any protective coatings per manufacturer instructions
Gasket Selection
- Choose gasket material compatible with process fluid
- Select gasket thickness appropriate for flange facing
- Ensure gasket pressure-temperature rating matches application
- Verify gasket dimensions (ID, OD, thickness) are correct
Bolt Selection and Installation
- Use bolts of appropriate material, grade, and length
- Install bolts with correct orientation (nuts facing accessible side)
- Apply lubricant to threads to achieve proper bolt stress
- Never reuse damaged, corroded, or elongated bolts
Bolt Tightening Procedure
- Follow proper cross-pattern tightening sequence
- Use calibrated torque wrenches for critical applications
- Apply torque in multiple passes (typically 30%, 60%, 100%)
- Verify final torque after system heat-up and cool-down
Alignment
- Ensure pipes are properly aligned before tightening
- Avoid using flange bolts to pull pipes into alignment
- Support piping adequately to prevent flange loading
- Verify flange faces are parallel within tolerance
Joint Assembly: Flanges Are Bolted Together
The fundamental principle connecting different types of flanges used in piping is that stainless steel flanges are joined to each other as they are bolted. This bolted connection creates a demountable joint that can be disassembled for maintenance, inspection, or modification without damaging the piping system.
The bolted assembly consists of:
- Two mating flanges (same size and pressure rating)
- A gasket compressed between the flange faces
- Bolts and nuts (or studs) passing through aligned bolt holes
- Proper bolt tightening creating the clamping force
This design allows stainless steel pipe flanges to provide secure, leak-tight connections while maintaining the flexibility to open the joint when needed—a critical advantage over welded or threaded connections in many applications.
Attachment Methods: How Flanges Connect to Piping
Stainless steel stub end flanges and other pipe flange types are attached to the piping system by either welding or threading, depending on the specific flange design and application requirements.
Welded Attachment Methods
Butt Welding: Used for weld neck flanges, requiring full-penetration groove welds that provide maximum strength and integrity.
Fillet Welding: Used for slip-on and socket weld flanges, requiring two fillet welds (inside and outside for slip-on, outside only for socket weld).
Stub End Welding: The stub end component is butt-welded to the pipe while the backing flange remains loose.
Threaded Attachment
Threaded flanges screw onto externally threaded pipes, creating mechanical connections without welding. This method is limited to smaller sizes and lower pressures but offers significant advantages where welding is prohibited or impractical.
Quality Assurance and Testing
Premium stainless steel pipe flanges undergo rigorous quality control:
Material Verification
- Positive material identification (PMI)
- Chemical composition analysis
- Mechanical property testing
- Heat treatment verification
Dimensional Inspection
- Diameter, thickness, and bolt hole measurements
- Face flatness and perpendicularity
- Bolt hole spacing and alignment
- Thread inspection (for threaded flanges)
Surface Finish
- Face finish verification (serration depth and pattern)
- Surface roughness measurement
- Visual inspection for defects
Non-Destructive Testing
- Magnetic particle or liquid penetrant testing
- Ultrasonic testing of forgings
- Radiographic testing where applicable
Pressure Testing
- Hydrostatic testing of completed assemblies
- Leak testing per applicable standards
Applications Across Industries
Oil & Gas
Different types of flanges used in piping throughout upstream, midstream, and downstream operations, including wellheads, manifolds, process equipment, and transmission pipelines.
Petrochemical
Chemical processing plants utilize various pipe flange types to handle corrosive fluids, high temperatures, and frequent maintenance requirements.
Power Generation
Conventional and nuclear power plants employ stainless steel flanges in boiler systems, steam lines, feedwater systems, and cooling circuits.
Chemical Processing
Diverse stainless steel pipe flanges accommodate aggressive chemicals, varying pressures and temperatures, and strict safety requirements.
Food & Beverage
Sanitary stainless steel flanges with electropolished finishes meet hygiene standards in dairy, brewing, and food processing.
Pharmaceutical
GMP-compliant pipe flange types ensure product purity in pharmaceutical manufacturing and bioprocessing applications.
Water Treatment
Municipal and industrial water systems use stainless steel pipe flanges for corrosion resistance in chlorinated and aggressive water service.
Marine & Offshore
Corrosion-resistant stainless steel flanges withstand harsh saltwater environments on ships, platforms, and offshore installations.
Maintenance and Inspection
Regular maintenance extends the service life of different types of flanges used in piping:
Routine Inspections
- Visual examination for corrosion, damage, or leakage
- Bolt tension verification
- Gasket condition assessment
- Alignment verification
Leak Management
- Immediate response to any detected leakage
- Proper retorquing procedures
- Gasket replacement when necessary
- Documentation of leak incidents
Preventive Maintenance
- Scheduled gasket replacement programs
- Bolt replacement on defined intervals
- Flange face inspection and refacing if needed
- Protective coating maintenance
Future Trends in Flange Technology
The evolution of pipe flange types continues with:
- Advanced materials including super-duplex and nickel alloys
- Improved gasket technologies for enhanced sealing
- Digital monitoring systems for leak detection
- 3D printing of custom flange configurations
- Enhanced surface treatments for extreme service
- Industry 4.0 integration for predictive maintenance
Arham Alloys: Your Trusted Steel Pipe Flange Partner
When it comes to sourcing premium-quality flanges for critical industrial applications, Arham Alloys stands as the best steel pipe flange supplier and manufacturer, delivering unmatched quality, comprehensive product range, and technical expertise to industries worldwide.
Comprehensive Flange Portfolio
Arham Alloys manufactures and supplies the complete spectrum of pipe flange types:
- Weld neck flanges in all sizes and pressure ratings
- Slip-on flanges including customized square and rectangular forms
- Socket weld flanges for small-bore applications
- Threaded flanges for no-weld installations
- Lap joint flanges with stub ends
- Blind flanges for closures and access points
- Orifice flanges for flow measurement
- Reducing and expander flanges
- Long weld neck and special flanges
Our extensive inventory of stainless steel pipe flanges spans sizes from 1/2″ NB to 48″ NB and beyond, ensuring immediate availability for urgent project requirements and routine maintenance needs.
Premium Material Selection
We supply stainless steel flanges in all grades:
- 304/304L, 304H for general applications
- 316/316L, 316Ti for enhanced corrosion resistance
- 321, 321H for high-temperature service
- 347, 347H for elevated temperature applications
- 310S for maximum heat resistance
- 317L for superior chemical resistance
- 904L for highly aggressive environments
- Duplex 2205 and Super Duplex 2507
- Nickel alloys (Inconel, Monel, Hastelloy)
Every material grade meets international standards including ASTM, ASME, DIN, BS, EN, JIS, and GOST specifications.
Manufacturing Excellence
As a premier manufacturer, Arham Alloys operates state-of-the-art production facilities featuring:
- Advanced forging equipment for superior grain structure
- Precision machining centers ensuring dimensional accuracy
- Heat treatment furnaces for optimal metallurgical properties
- Surface finishing capabilities including electropolishing
- In-house testing laboratories with advanced equipment
Our manufacturing processes produce stainless steel pipe flanges meeting exact specifications for all different types of flanges used in piping applications.
Standards Compliance
Arham Alloys manufactures flanges conforming to:
ANSI/ASME Standards: B16.5, B16.47 Series A & B, B16.48 European Standards: BS 4504, BS 10, EN-1092, DIN Asian Standards: JIS, GOST Pressure Ratings: All classes from 150 LBS to 2500 LBS, PN6 to PN64, 5K to 63K
Quality Assurance
Every stainless steel flange undergoes rigorous quality control:
- Complete material traceability from mill to final product
- Positive material identification on every piece
- Dimensional verification against applicable standards
- Non-destructive testing (PT, MT, UT) as required
- Hydrostatic testing of assemblies
- Third-party inspection services available
- ISO 9001:2015 certified quality management system
Technical Expertise
Our experienced engineering team provides comprehensive support:
- Material grade selection for specific applications
- Pressure-temperature rating verification
- Gasket selection recommendations
- Custom fabrication design assistance
- Installation guidance and best practices
- Troubleshooting and problem resolution
Competitive Advantages
Choosing Arham Alloys provides distinct benefits:
Extensive Inventory: Ready stock of commonly used pipe flange types enables quick delivery and reduced project lead times.
Custom Capabilities: In-house fabrication produces special flanges, customized dimensions, and unique configurations including square and rectangular slip-on flanges.
Competitive Pricing: Efficient operations and strong supplier relationships enable premium quality at competitive prices.
Global Supply: Robust logistics network ensures timely delivery domestically and internationally.
Complete Documentation: Every shipment includes mill test certificates, material traceability, dimensional reports, and required certifications.
After-Sales Support: Our commitment extends beyond delivery with ongoing technical assistance and warranty support.
Industry Experience
Arham Alloys supplies stainless steel flanges across diverse sectors:
- Oil & Gas: Refineries, pipelines, offshore platforms
- Petrochemical: Process plants, storage facilities
- Chemical: Manufacturing and processing facilities
- Power Generation: Thermal, nuclear, renewable energy
- Pharmaceutical: API manufacturing, formulation plants
- Food & Beverage: Processing and packaging operations
- Water Treatment: Municipal and industrial systems
- Marine: Shipbuilding and offshore installations
Our deep industry knowledge ensures appropriate recommendations and specifications for each sector’s unique requirements.
Commitment to Excellence
At Arham Alloys, we don’t just supply flanges—we deliver solutions. Our reputation as the best steel pipe flange supplier and manufacturer is built on:
- Uncompromising quality standards across all pipe flange types
- Technical competence and innovation
- Customer-centric approach and responsive service
- Ethical business practices and transparency
- Continuous improvement philosophy
- Environmental responsibility and sustainability
Whether you need standard stainless steel pipe flanges for routine applications or specialized different types of flanges used in piping for critical projects, Arham Alloys provides the quality, expertise, and service that leading industries demand.
Contact Arham Alloys today to discuss your stainless steel flange requirements. Experience the difference that quality, technical expertise, and dedication make in your projects. Discover why industry leaders choose Arham Alloys as their trusted partner for premium pipe flange types and piping components.